Buyer's Guide
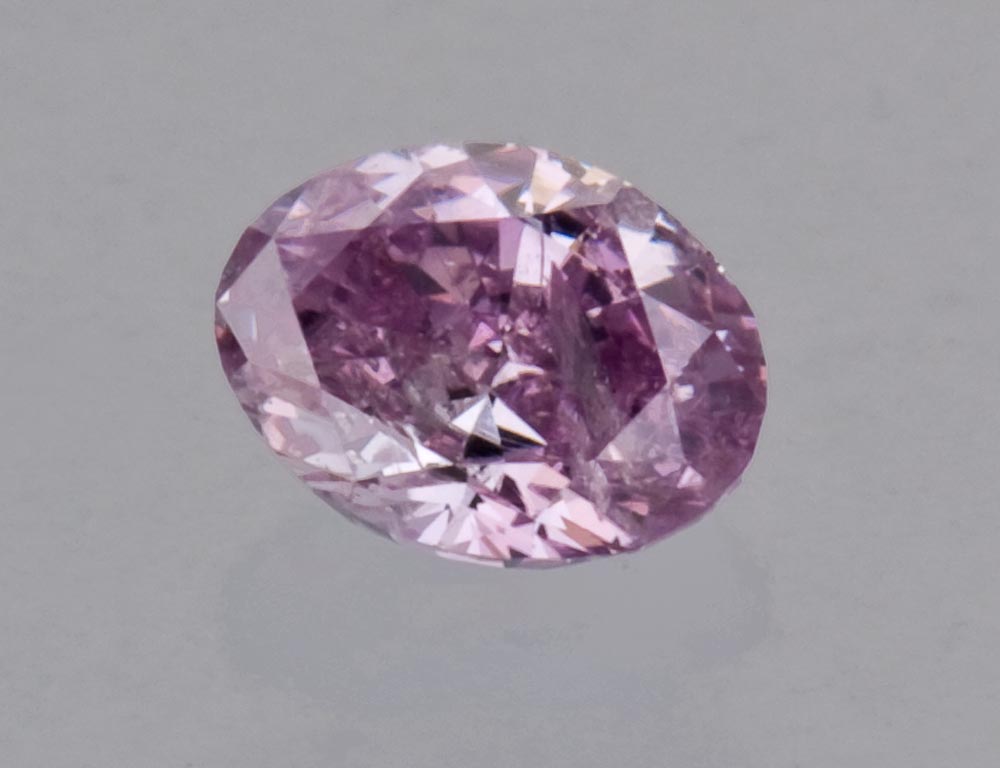
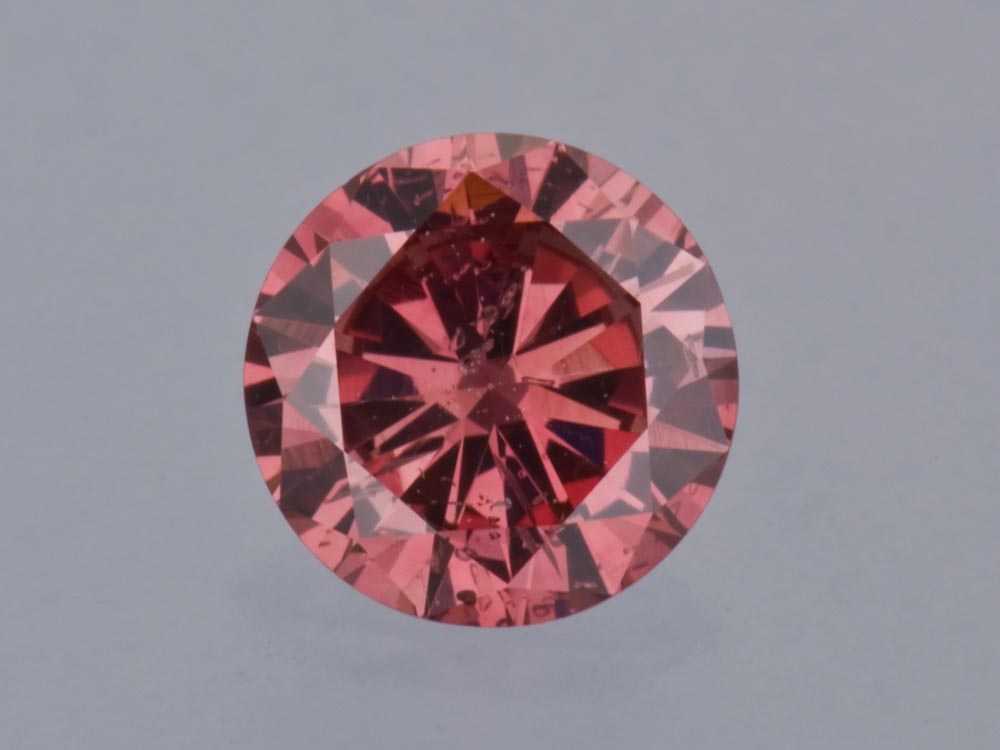
With fancy color diamonds the rarest, most valuable colors are saturated pinks, blues, and greens. Even very slight color differences can have a big impact on value.
FIND A JEWELER
Submit your gemstone through your local jeweler.
FIND A REPORT
Verify the information on your report matches what is archived in the GIA report database.
What To Look For
Compared to fancy yellows and browns, diamonds with a noticeable hint of any other hue are considerably more rare. Grading fancy color diamonds is complex and specialized, and it takes highly trained laboratory graders to complete the process accurately.
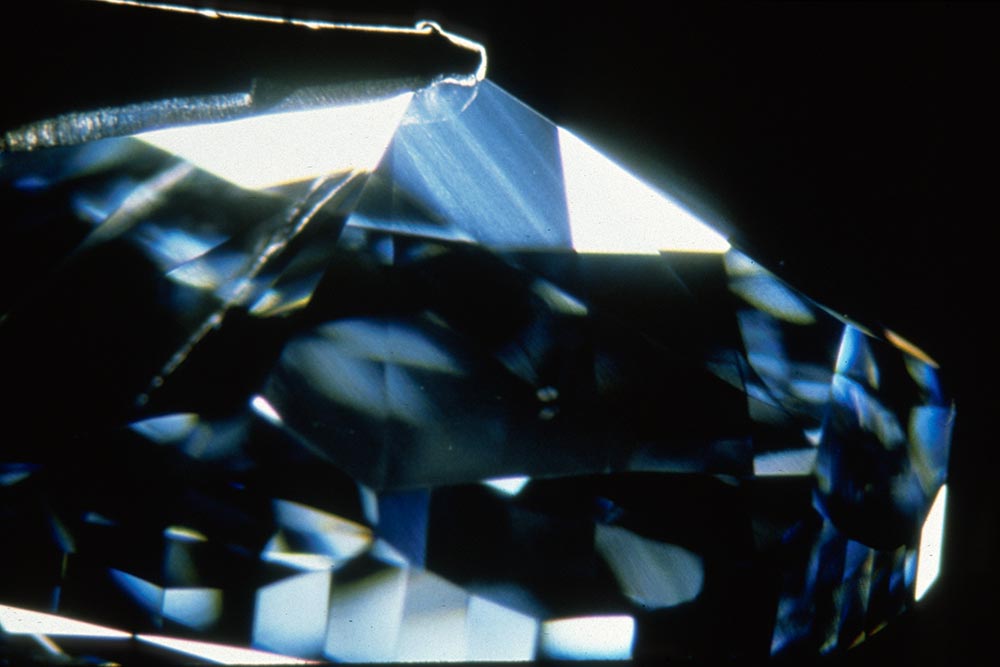
Color is the dominant value factor. Even diamonds with numerous inclusions that result in a low clarity grade are prized by connoisseurs if they display attractive face-up color. Of course, inclusions that threaten the gem’s durability can lower a fancy-colored diamond’s value significantly.
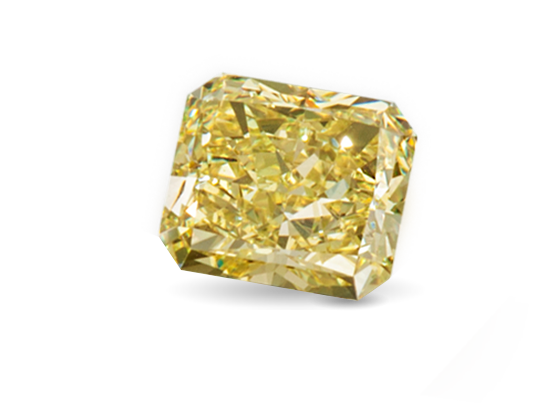
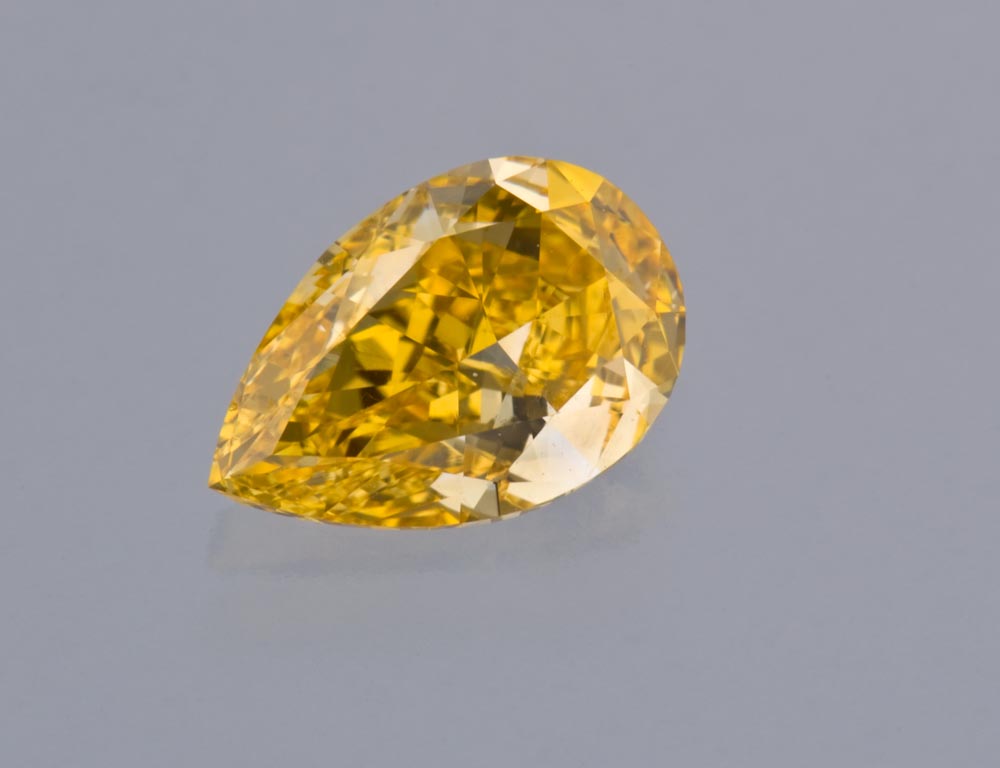
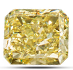
Cutters discovered that certain styles—typically mixed cuts like the radiant—can intensify yellow color in diamonds that are toward the lower end of the D-to-Z color-grading scale. When carefully fashioned as radiant cuts, many yellow-tinted stones can become fancy yellows when viewed face up.
Fancy Color Diamond Quality Factors: The Comprehensive Guide
Questions & Answers
When is a colored diamond a fancy color diamond?
When a diamond falls outside of GIA’s D-to-Z color scale, it is considered a colored diamond (sometimes called a fancy-color diamond). This includes all colors other than colorless to light yellow or brown. On GIA Colored Diamond Grading Reports, colored diamonds are graded in order of increasing color strength, from Faint, Very Light, Light, Fancy Light and Fancy to Fancy Intense, Fancy Vivid, Fancy Dark and Fancy Deep. Fancy Intense and Fancy Vivid generally command higher prices.
What cut proportions are best for a fancy color diamond?
Colored diamonds are usually cut to maximize the intensity of their color rather than to maximize light return. The best cut is one that gives the most attractive face-up color.
What are black diamonds?
The opaque color of black diamonds is caused by dark inclusions or, more commonly, by color treatment. Most black diamonds are treated to become a green that’s so dark it appears black, but not opaque.
Why are there three kinds of GIA colored diamond reports?
The GIA Colored Diamond Grading Report contains the same comprehensive diamond 4Cs information as the GIA Diamond Grading Report. The GIA Colored Diamond Origin Report contains the same comprehensive diamond 4Cs information as the GIA Colored Diamond Grading Report as well as providing the geographic origin of the diamond. The GIA Colored Diamond Identification and Origin Report (the “color-only report”) is limited to color grade and the origin of the color (natural or treated). Click here to view a full detailed report comparison of the three kinds of GIA colored diamond reports.
When does yellow become a positive color factor?
Most diamonds used in jewelry range from colorless to light yellow and are graded on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow). Those with less color, or closer to colorless, are generally more valuable. Diamonds with deeper shades of yellow (more color than Z) are graded differently and given a fancy-color grade. For these colored diamonds, a more vibrant color typically means higher value.
Find out more
Fancy Color Diamond: Questions & AnswersCaring for Your Fancy Color Diamond
Keep your fancy color diamond beautiful by following simple care and cleaning guidelines.

Durability
Sudden temperature changes can cause thermal shock and create or extend fractures and cleavages.

Care and Cleaning
Warm soapy water is always safe.

Treatment
Diamonds can be treated to alter their color. Treatments range from primitive to very high-tech.